Solar Energy Explained: Benefits, Components, and How It Works
Renewable Solar Energy
Energy can be harnessed from natural, nearly limitless sources that replenish themselves naturally. This is known as renewable energy, also referred to as clean energy or green energy.
Different types of renewable energy sources include solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, hydroelectric, ocean energy, and bioenergy.
What is Solar Energy?
Any form of energy derived from the sun is called solar energy. This energy is captured from sunlight and converted into usable solar power. The technologies that convert solar energy are known as solar energy systems.
Types of Solar Energy Systems
There are two main types of solar energy technologies:
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV): One of the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies, it converts sunlight directly into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Solar Thermal Energy: This technology uses the sun’s heat to generate warmth or produce electricity.
Adopting sustainable energy solutions helps protect the environment and positively impacts the planet.
Be a Part of the Change – Switch to Solar Energy Today!
How Does Solar Energy Work?
- When sunlight falls on a solar panel, it absorbs the energy and excites electrons to generate direct current (DC) electricity.
- An inverter converts DC into alternating current (AC), making it usable for homes and electrical appliances.
- The AC electricity is then used for household needs or fed into the power grid.
- A net meter records incoming and outgoing electricity, ensuring that users only pay for the net consumed units, reducing electricity bills.
- The grid acts as a supply network, allowing excess electricity to be sent to the grid and drawing power when needed.
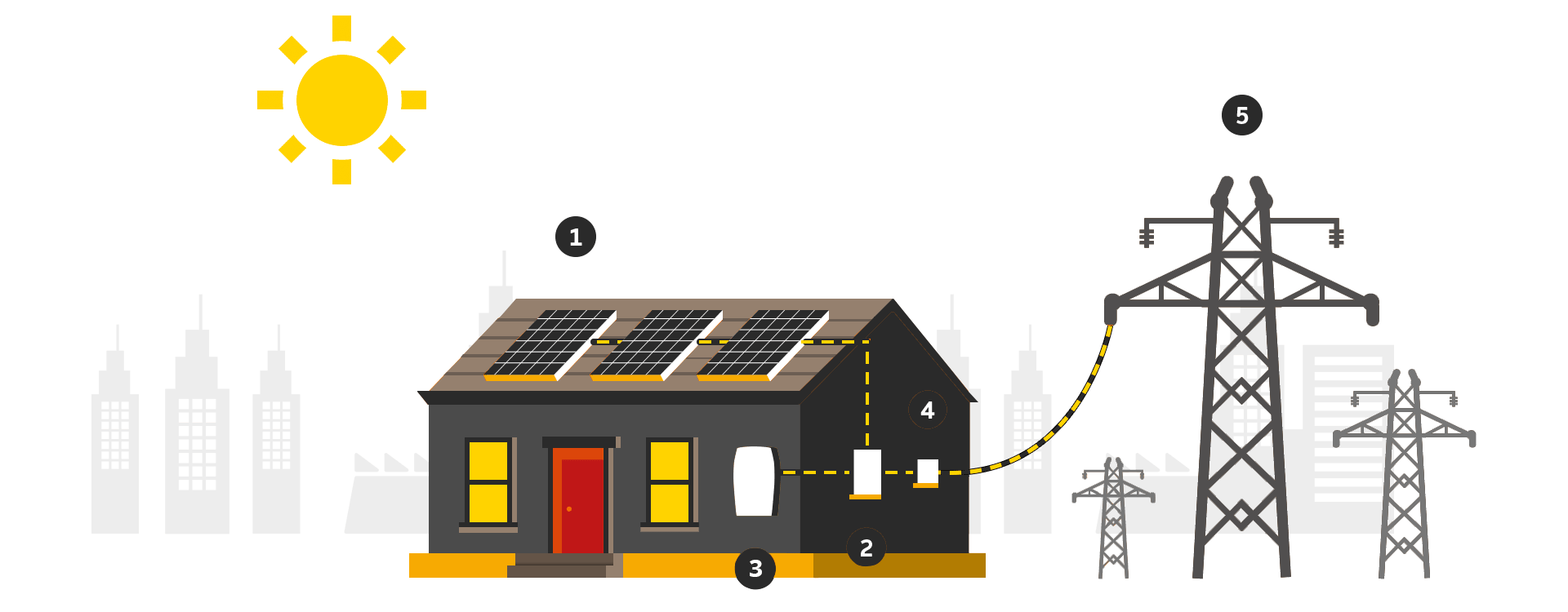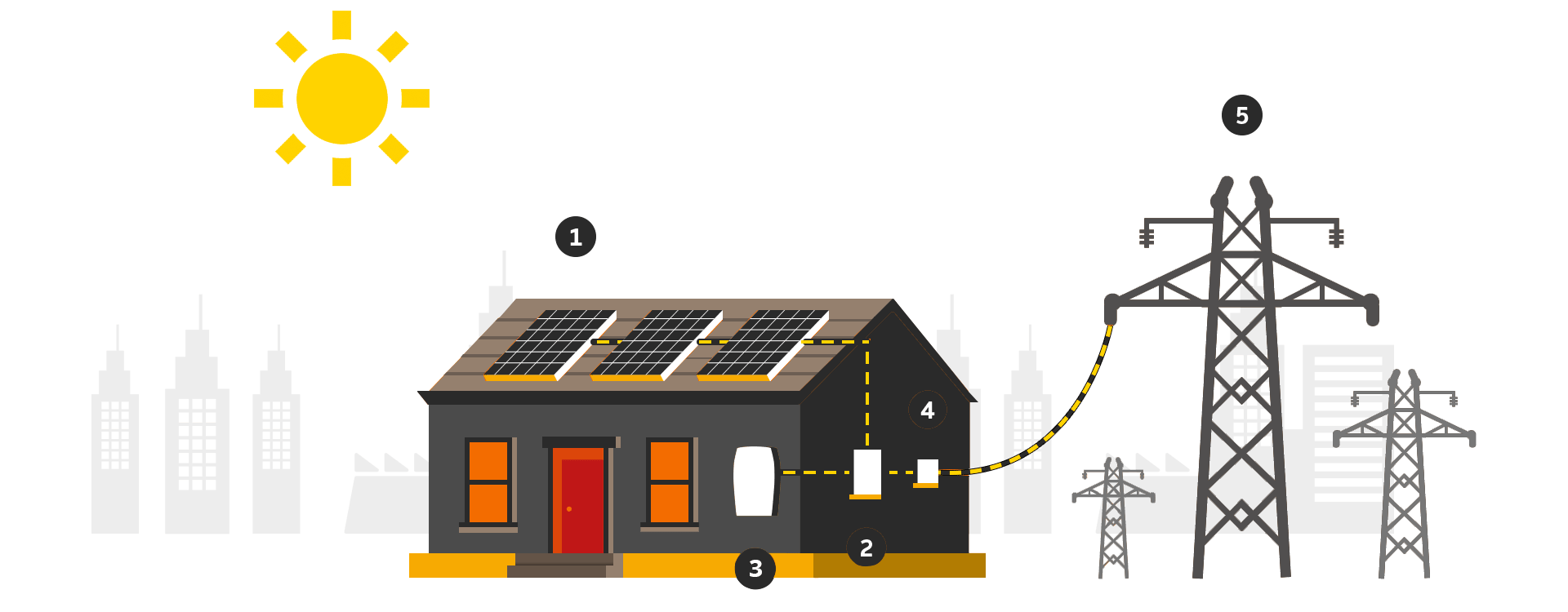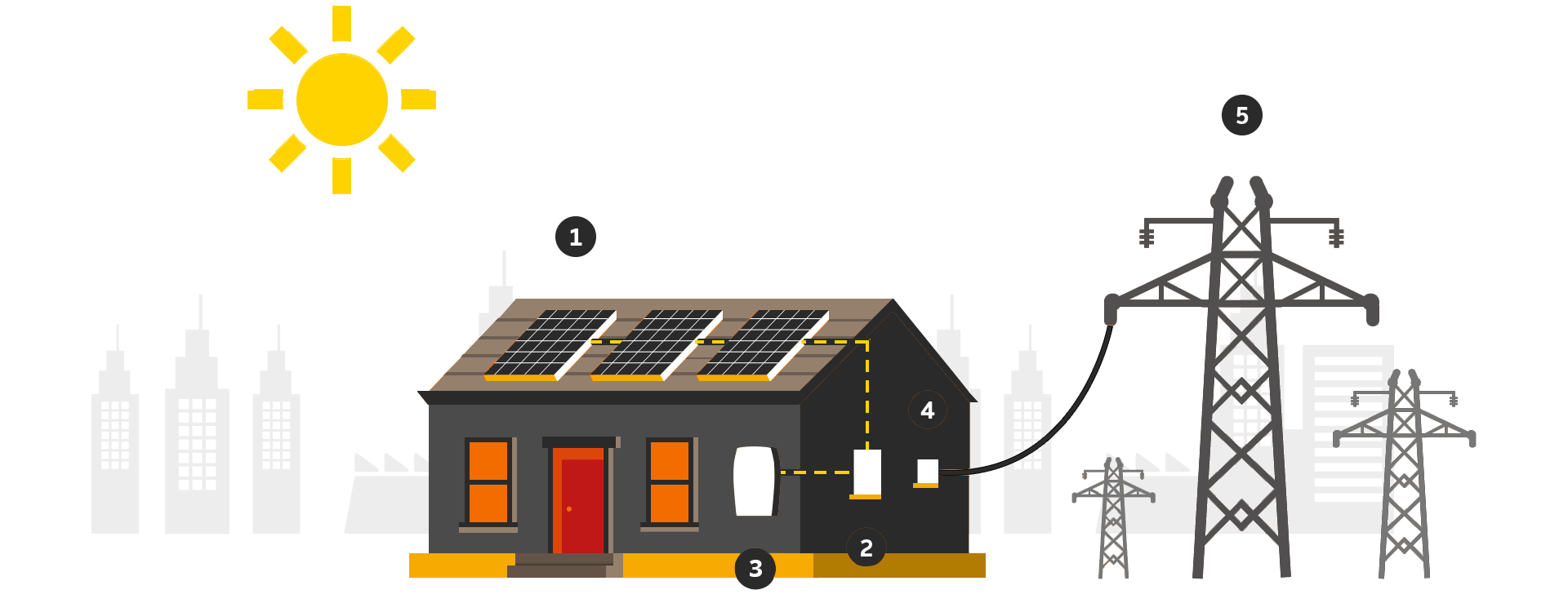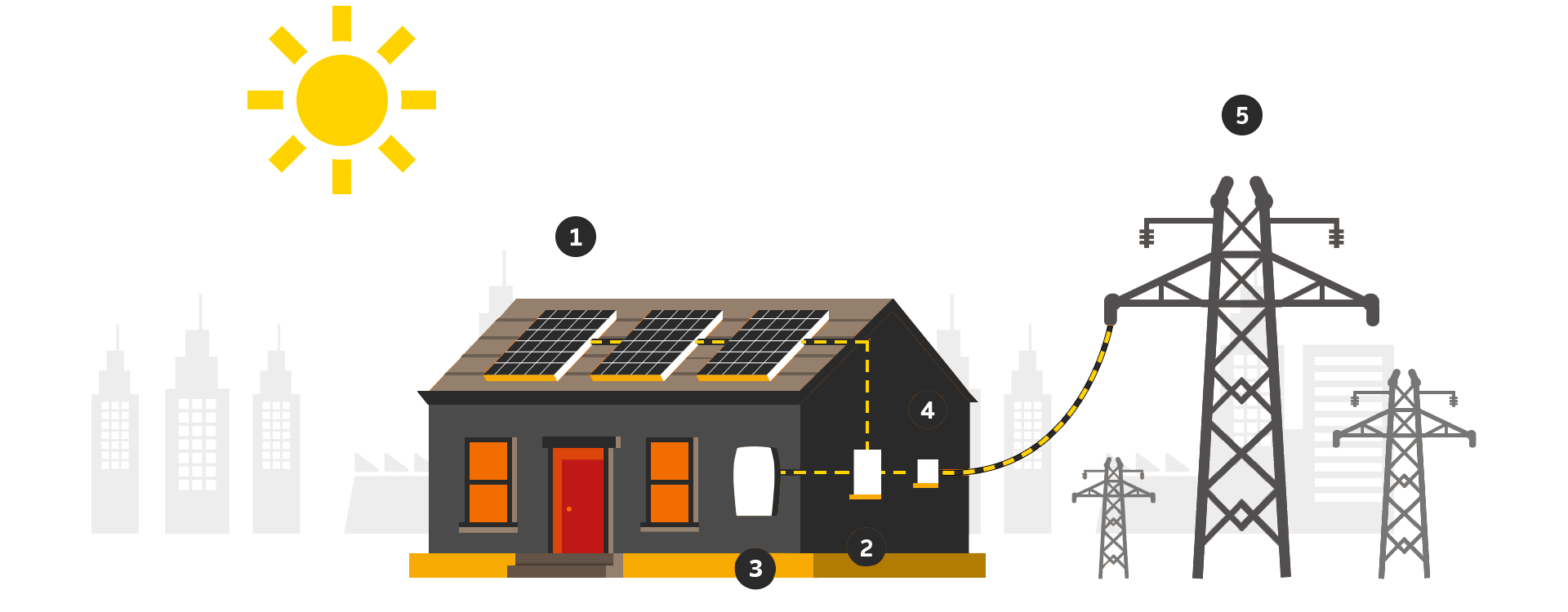
Components of a Solar Energy System
1. Solar Panels
Made of silicon, they convert sunlight into electricity and are typically installed in unshaded, south-facing locations (often rooftops).
Types of Solar Panels:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Highest efficiency (19-20%), made of pure silicon, but expensive.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Made of multiple silicon crystals, more affordable but with lower efficiency (14-16%).
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: Lightweight, easy to install, but less efficient and cost-effective.
2. Inverter
Converts DC electricity from solar panels into AC electricity for safe home use.
3. Solar Panel Mounting Structures
These hold solar panels in place for maximum solar radiation exposure and must be weather-resistant to withstand floods or storms.
4. Solar Tracker
Adjusts the panels to follow the sun’s movement, increasing energy production.
5. Bi-Directional Meter (Net Meter)
Measures the electricity imported from and exported to the grid. Under India's solar net metering policy, users pay only for the difference between imported and exported electricity.
6. Distribution Box (DB)
Controls electricity flow and ensures safety.
- Solar ACDB (Solar AC Distribution Box): Installed between the inverter and electrical appliances.
- Solar DCDB (Solar DC Distribution Box): Installed between the solar panels and inverter.
7. Grid
A network of devices and cables that stores and distributes generated energy. If excess electricity is produced, it is supplied back to the grid for future use.


0 Comments